The NIS2 Directive, officially known as the Network and Information Security Directive, is a significant piece of European Union (EU) wide cybersecurity legislation. It was introduced to bolster cybersecurity across the EU and protect critical infrastructure. Effective from January 2025, with transposition into national laws required by October 2024, the directive imposes stringent compliance measures, including financial penalties and potential consequences for C-level executives.
As the specific requirements remain unclear, organizations face uncertainty in preparing for compliance. This article explains how Maltego can support businesses in enhancing cybersecurity measures, including risk assessment, incident investigation, and information gathering, to help navigate the challenges posed by the NIS2 Directive. Get the complete picture now!
Evolution of the NIS2 Directive 🔗︎
To grasp the NIS2 Directive, let us first understand the original NIS Directive of 2016, the first EU-wide cybersecurity legislation. Enacted on July 6, 2016, as Directive (EU) 2016/1148 by the European Parliament and the Council of Europe, its aim was to enhance cybersecurity and risk management for organizations that provide services essential to our economy and society, particularly those that heavily depend on information and communication technologies (ICTs), such as energy, transportation, water, banking, financial market infrastructures, healthcare, and digital infrastructure.
Between 2016 and 2018, efforts persisted to develop this foundational cybersecurity legislation, garnering substantial industry interest as it represented the inaugural EU-wide legislative effort in this field.
Why do we now have a second version? The COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 caused significant disruption, accelerating digital transformation and reshaping the threat landscape with a substantial increase in cybercrime. High-impact data breaches, such as the SolarWinds attack, affected supply chains and critical infrastructure providers. Additionally, the EU noticed inconsistencies in how member states applied the directive, particularly in defining which organizations qualify as essential operators and digital service providers. There was also insufficient common understanding of the main threats and challenges. This recognition led to the revision of the directive.
In conclusion, the NIS2 Directive (Directive 2022/255) was published on January 16, 2023, to make the regulations more specific and thorough. It mandates that every member state harmoniously transposes to stricter regulations by the deadline of October 17, 2024. The primary goal of this second version is to reduce inconsistencies by covering a broader range of organizations and implementing stricter requirements and liability provisions for the management of affected organizations. Wondering if your business falls under the scope of the NIS2 Directive? Explore more below!
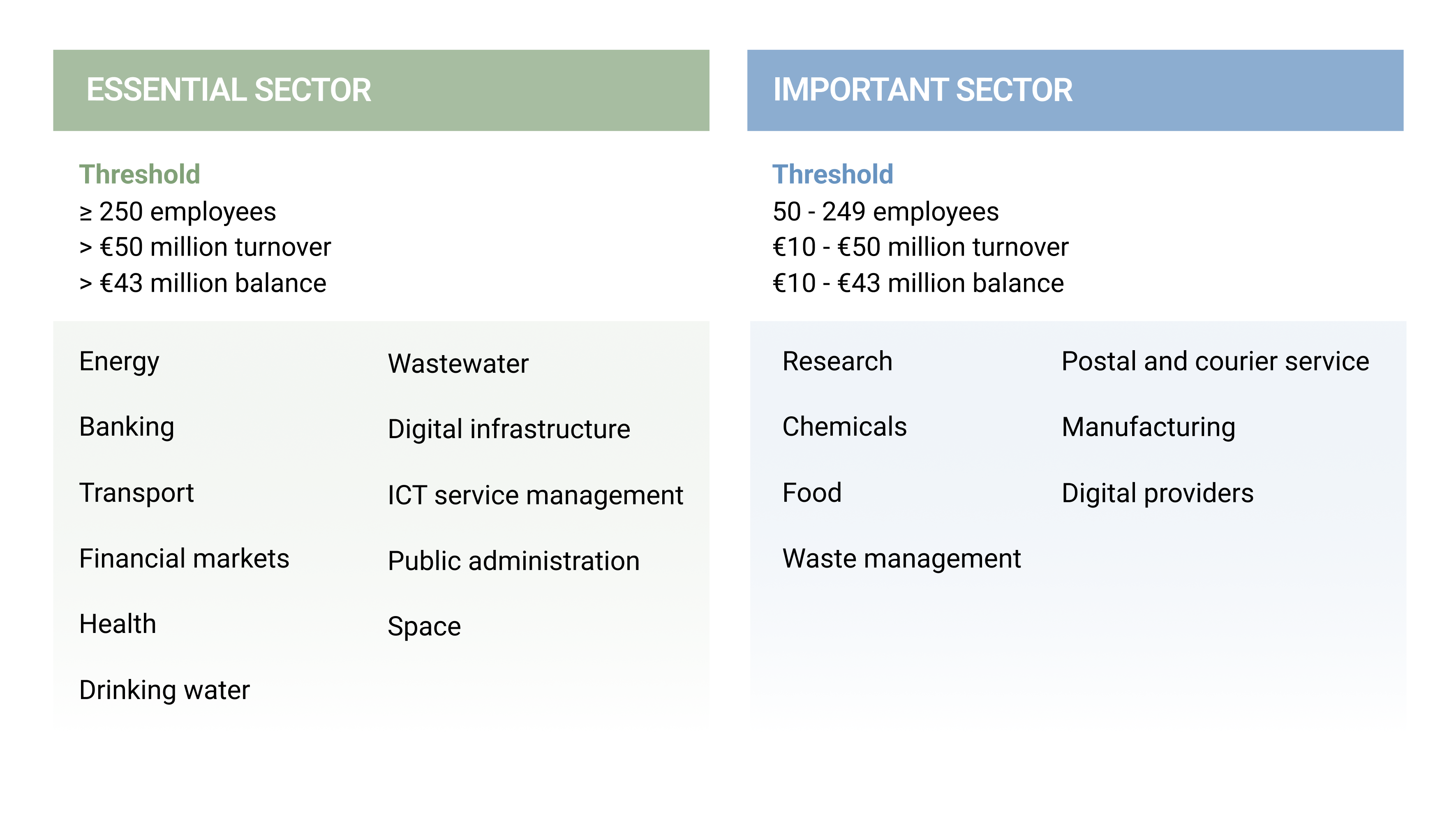
Sectors in Scope 🔗︎
This categorization aims to ensure that sectors vital to the economy and society are better protected against cyber threats. The NIS2 Directive, covered by two annexes, expands the scope of the original NIS Directive to include more sectors and types of entities, reflecting the growing interconnectedness and digitalization of critical infrastructure. Annex I lists the high criticality sectors, which can be classified as either “Essential” or “Important” entities based on the industry type, number of employees, annual turnover, and balance of the organization.
Additional Notes:
- Specific to certain services: There are sectors dedicated to specific services, such as Trusted Service Providers, which include electronic identification and trust services, DNS and name registries, and public communications networks or publicly available electronic communication services.
- Entities within these sectors need to comply with the NIS2 directive’s requirements for cybersecurity risk management and incident reporting.
- Important entities include those from other critical sectors but with slightly different obligations compared to Essential entities.
REMARK Please note that an entity exceeding the threshold for the “Important” sector but not meeting the criteria for the “Essential” entity must comply with this law as an “Important” enterprise. A detailed and designated list of operators of essential services and digital service providers can be found here. For more FAQs related to the NIS2 Directive click here.
Enhancing NIS2 Compliance with Maltego 🔗︎
Every business relies on a digital network and technology stack consisting of multiple platforms and providers, all of which are heavily interconnected. The CrowdStrike incident is a prime example of how one security event can severely impact others, causing billions in financial losses across various industries. Following this incident, we’ve seen malicious forces take advantage of the crisis, striking when targets are most vulnerable.
This highlights the critical need for many businesses to bolster their cyber resilience and collaborate with other sectors. While using Maltego alone does not directly ensure compliance with the NIS2 Directive, it can be an essential component of a broader toolkit that supports NIS2 compliance in areas such as risk assessment and management, incident response and forensic investigations, and information sharing.
For instance, the entire initiative focuses on effective risk management and incident response posture to mitigate risks associated with network and information systems. It also emphasizes the importance of reporting incidents in a timely and accurate manner to relevant authorities. Maltego can help map the digital footprint of an organization, identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities more comprehensively. By enabling real-time data collection and visualization, Maltego assists in the quick identification, triage, and analysis of incidents.
In the whitepaper, we detail more examples of how Maltego can enhance compliance with the NIS2 Directive in key regulatory areas.
Download the Whitepaper for Full Insights! 🔗︎
Understanding and adhering to the NIS2 Directive is not just a regulatory necessity; it is a critical step in bolstering cybersecurity defenses. Integrating Maltego into cybersecurity strategies allows organizations to strengthen their defenses and adhere more closely to the stringent requirements of the NIS2 Directive. This alignment not only ensures compliance but also enhances overall cyber resilience, providing a comprehensive approach to managing cybersecurity risks. Download the white paper to find more out about how Maltego enhances NIS2 compliance, guidance on how to prepare your organizations, and the importance of threat intelligence in regulatory compliance.
Download the white paper to learn more about how Maltego enhances NIS2 compliance, provides guidance on preparing your organization, and emphasizes the importance of threat intelligence in regulatory compliance.
Download the resource
Stay connected with us on X and LinkedIn, and subscribe to our email newsletter to stay updated with the latest news and developments.
Happy investigating!