KEY POINTS: 🔗︎
- Structured Analytic Techniques (SATs), such as the Key Assumptions Check (KAC) and Red Team Analysis (RTA), assist analysts in critically examining information and mitigating biases amid the growing challenges posed by threat actors.
- The effectiveness of the KAC lies in its ability to yield immediate and valuable results. By allowing analysts to scrutinize assumptions, identify flaws, and promote transparency and logical reasoning, it enhances the analytic process.
- RTA enables analysts to break free from established mental frameworks, but its execution requires careful planning, challenging institutionalized beliefs, and assessing plans from different perspectives.
Introduction 🔗︎
As threat actors continue to adapt and excel in complex environments, countering them has become increasingly challenging, often leaving those who seek to hunt them lagging behind. This puts pressure on analysts to work more effectively and efficiently to produce valuable intelligence results.
Generating intelligence in the face of this adaptability becomes an arduous task characterized by a rigorous selection, evaluation, interpretation, and expression process. On top of that, intelligence analysis is susceptible to human fallacies that can impair judgment and undermine conclusions.
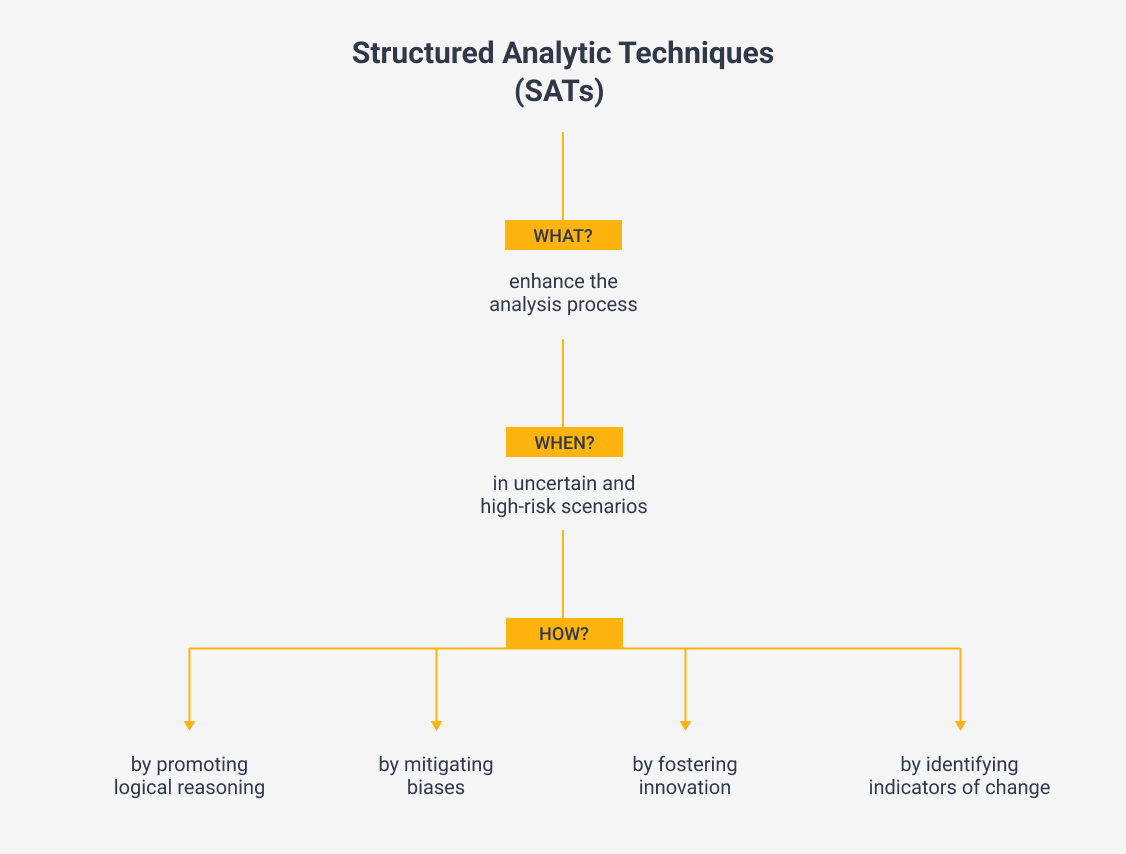
To elevate the structure of the analytic process and keep pace with changing circumstances, analysts can employ Structured Analytic Techniques (SATs) which we will evaluate in this article.
What are Structured Analytic Techniques? 🔗︎
While the concept of using SATs to meet analytic needs is not a new one, it was not until the attacks of September 2001 that the cost of intelligence failures in the modern world was brought into the public sphere.
This revelation made it evident that intelligence analysis itself has significant limitations, which could have critical implications.
Ultimately, a set of Structured Analytic Techniques was established to help alleviate common analysis failures by:
- Accelerating analysis with a formalized framework for information processing
- Implementing quality gates and checks to ensure objectivity
- Laying the foundation for critical analysis, leading to self-reflection and processual improvements
By utilizing SATs, we can enhance the way in which we analyze information, ensuring our conclusions are well-structured and based on logical reasoning. SATs also help to overcome cognitive biases, foster creativity in our thinking, and identify early warning signs of change, which are crucial in uncertain and high-stakes situations.
Numerous SATs have been identified over the past decades, but we will narrow our focus to two specific examples in this article: the Key Assumptions Checks (KAC) and Red Team Analysis (RTA).
What are Key Assumptions Checks? 🔗︎
The Key Assumptions Checks aim to enhance the transparency of analytic arguments and assumptions regarding intelligence gaps.
It is about dedicating time, either individually or as a group/team, to identify, elaborate upon, and review the key assumptions that have been made.
The KAC methodology follows a four-step process:
In brief, KAC will enable us to critically examine and gain a deeper understanding of crucial aspects within an investigation. This includes analyzing individual data points and the connections between them.
The KAC technique requires minimal setup, is straightforward to use, and can yield immediate and valuable results.
It is particularly valuable when applied at the outset of an analytic project, although it can also be implemented at various stages throughout the analysis process prior to reaching a conclusion.
Key Assumptions Checks in Practice 🔗︎
To demonstrate the practical application of this SAT, let’s examine the 2002 DC Sniper Case. During this period, a series of shootings took place, claiming the lives of 17 individuals and injuring 10 others over 10 months.
When law enforcement initially analyzed the incident, they made several critical assumptions:
- The sniper was male.
- The sniper was acting alone.
- The sniper was white.
- The sniper had military training.
- The sniper was driving a white van.
A critical analysis of these assumptions would reveal the following points of contention:
- While most similar incidents in the US involve white, male, solo actors, excluding non-white and female suspects would greatly limit the suspect pool.
- Military training, while plausible, is not a certainty as private citizens also have access to firing ranges.
- Relying solely on one witness report of a white van speeding away prematurely narrows down the potential suspects.
Ultimately, the “DC sniper” case resulted in the detention of two men of Jamaican heritage who were charged with the crimes. One of them did have military training, but they used a blue Chevrolet for the attacks instead of the assumed white vehicle.
Out of the five initial assumptions, only two proved to be correct. If these assumptions had been properly scrutinized, the investigation could have proceeded in a more comprehensive manner, and although more suspects would have been considered, this ‘wider net’ could have included the perpetrators thus bringing the case to a close much sooner.
The KAC technique could have been employed with minimal effort and yielded significant results. In similar cases, other SATs can also be applicable. For example, Red Team Analysis.
What is Red Team Analysis? 🔗︎
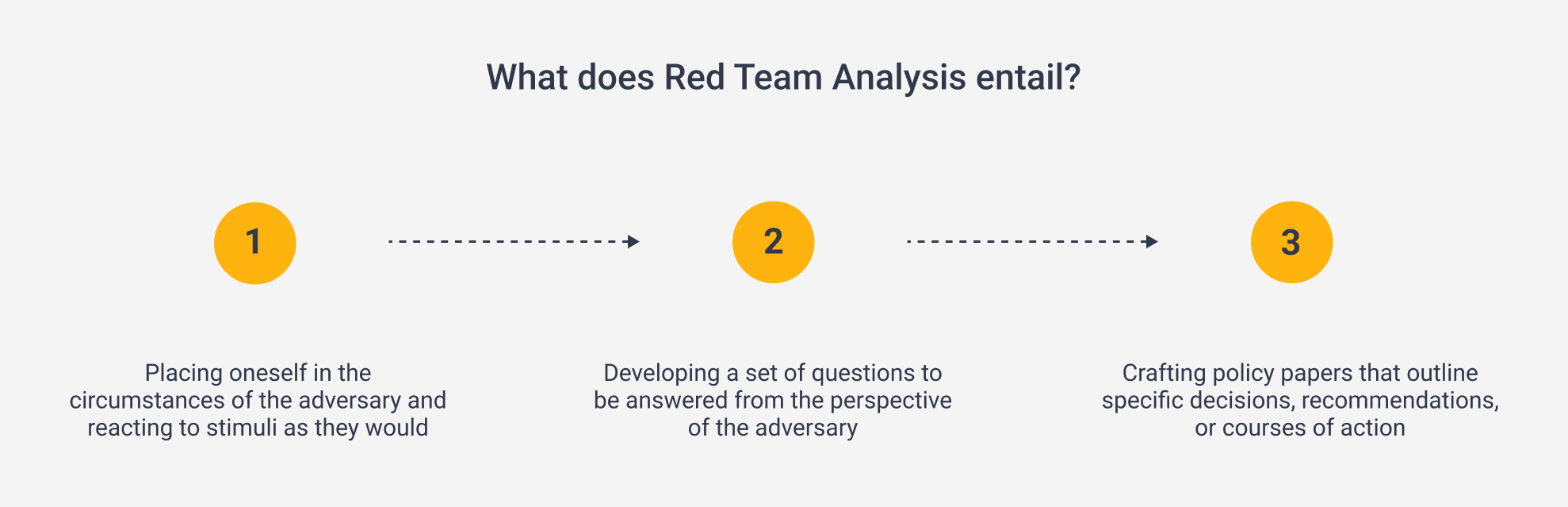
Red Team Analysis can be likened to a pattern of imaginative thinking, aimed at generating fresh insights, alternative perspectives, and different outcomes.
By adopting RTA, analysts can break free from their established mental environment and transition from being mere observers of an adversary to assuming the role of the adversary themselves. This involves considering the cultural norms, personal values, and rationality of the adversary they seek to emulate.
On the whole, RTA does not have clear and concise steps but rather seeks to establish an environment in which the technique can be leveraged. The ultimate goal is to assess the operation’s vulnerabilities and weaknesses from an opposing perspective, as well as helping to identify blind spots and potential flaws in a given plan.
An example of effective Red Teaming is Operation Desert Storm, where RTA was utilized to simulate and assess potential Iraqi strategies and tactics, which in turn led to improved operational planning and decision-making.
In its nature, the role of RTA is to:
Red Team Analysis in Practice 🔗︎
RTA is a complex and context-dependent technique to plan and execute. In the book Enhancing and Developing a Red Teaming Community in MORS, Kardos and Dexter identified seven different types of Red Teaming activities, including:
- Field/Deployment Exercises
- Wargaming
- Cyber
- Computational
- Functional/CPX
- Discussion/Tabletop Exercises
- Critical Analysis
In terms of technical considerations, there are a few requirements to consider:
- The perspective and approach for each of these activity types need to be defined and planned to create the framework and boundaries for the exercise.
- Participant selection is critical to achieving ideological neutrality to maintain objectivity because a biased team may suppress dissent rather than engage in substantive debate.
- Given the nature of RTA and its requirement to understand the adversary’s mindset, intimate knowledge of adversarial tactics, technology, political climate, forces, systems, and values is necessary.
It is important to note that the expertise needed for RTA may surpass the capabilities of regular intelligence analysts and require experienced subject matter experts, such as university professors.
How Can SATs Help Shape Better Intelligence Analysis? 🔗︎
Both the Key Assumptions Check (KAC) and Red Team Analysis (RTA) provide valuable techniques for intelligence investigations, but their effectiveness relies on systematic, rigorous, and regular application.
Instead of simply mandating their teaching to analysts, it is advisable to invest time and resources in evaluating their usefulness to prevent SATs from complicating the analytic process rather than providing clarity.
In the longer term, prioritizing the understanding of SATs before implementation will support the professional growth of intelligence analysts and equip analysts with critically analyzed and effective techniques.
To read the complete essay about evaluating SATs, download Aaron’s original paper here:
Download the resource
If you found this article useful and would like to see more updates on intelligence gathering or other related topics, you can follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn, or subscribe to our newsletter.
Happy investigating!
About the Author 🔗︎
Aaron Dixon 🔗︎
Aaron Dixon is a former member of the New Zealand Military who has spent the last 6 years working as a consultant in the areas of IT Security and Compliance, Data Privacy, Digital Forensics and Cyber Threat Intelligence. He holds a bachelor’s degree with a double major in History and Defense Studies, as well as a Postgraduate Certificate in International Security. His primary areas of interest are terrorism and geopolitical conflict, as well as focusing on the foundational processes and principles of the Intelligence Cycle.
Sources 🔗︎
- Greenberg, A. (1981). An Outline of Wargaming. Naval War College Review, 34(5), 93–97.
- Coulthart, S. J. (2017). An Evidence-Based Evaluation of 12 Core Structured Analytic Techniques. International Journal of Intelligence and Counterintelligence, 30(2), 368–391.
- Kardos, M., Dexter, P., & Bowden, F. D. J. (2016). Enhancing and Developing a Red Teaming Community in MORS. Phalanx, 49(4), 20–22.
- Marrin, S. (2009). Training and Educating U.S. Intelligence Analysts. International Journal of Intelligence and Counterintelligence, 22(1), 131–146.
- Moore, D. T. (2007). Critical Thinking and Intelligence Analysis. National Defense Intelligence College Occasional Paper 2007(1). Washington, D.C.: National Defense Intelligence College.
- Moran, J. P. (2021). Red Team or Red Herring? Lessons Learned from the Policy Counter Terrorism Evaluation Group. The International Journal of Intelligence, Security, and Public Affairs, 23(3), 400–424.
- Pherson, R. H., & Heuer, R. J. Jr. (2014). Structured Analytic Techniques: A New Approach to Analysis. In R. Z. George & J. B. Bruce (Eds.), Analyzing Intelligence: National Security Practitioners’ Perspectives (2nd ed., pp. 444–477). Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press.
- Reinhold, D., Russo, C., & Eisenfeld, B. (2020). Analytical Standards in the Intelligence Community: Are Standards Professionalized Enough? Journal of Strategic Security, 14(1), 106–121.
- United States Government. (2009). A Tradecraft Primer: Structured Intelligence Techniques for Improving Intelligence Analysis. Washington, DC.

 4.5 rating
4.5 rating