For the cyber intelligence community, MITRE ATT&CK has become the standard for modeling and communicating adversarial tactics and techniques based on real-world observations. Provided and maintained by the MITRE organization, the ATT&CK Matrices are enabling numerous communities to develop more effective cybersecurity practices.
Introduction 🔗︎
Many organizations run MISP instances with other cybersecurity tools and OSINT for data-driven investigations. Investigators can integrate internal and external data to map with MISP data in various ways. This blog details how to look up information directly in the MISP community using MISP Transforms on Maltego Graph, highlighting its seamless integration for efficient and comprehensive investigations.
How Maltego Integrates with MISP Data 🔗︎
Requirements 🔗︎
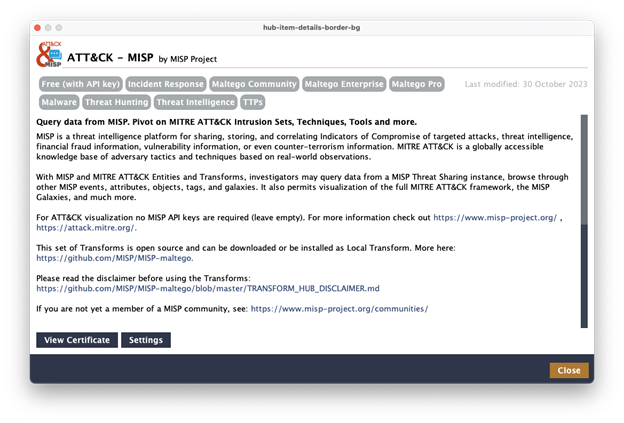
API access to MISP instance(s) and MISP-Maltego Library. Pre-requisites and installation instructions are available on GitHub here. Alternatively, if your MISP instance is internet-facing, you can use the integration provided by Maltego. Simply install the “ATT&CK – MISP" Hub item and enter your login information under Settings.
Use Cases 🔗︎
With MISP and MITRE ATT&CK Entities and Transforms on Maltego Graph, investigators can query data directly within the same interface during investigations, achieving faster clarity while improving workflow efficiency. They can explore MISP threat-sharing instances, events, attributes, objects, tags, and galaxies for a solid starting point for further exploration. Typical use cases include:
- Query MISP Datasets: Seamlessly query MISP datasets within Maltego Graph to enhance your investigations with valuable threat intelligence. For instance, query a MISP instance for events containing a specific Indicator of Compromise (IoC).
- Visualize Connections: Visualize and map relationships between MISP data and other OSINT sources to uncover hidden patterns or connections that might have gone unnoticed. For example, pivot a MISP event into its attributes, objects, tags, galaxies, and related events.
- Enrich Entities: Enrich Entities discovered during investigations with relevant MISP data, providing additional context and insights into data. For example, explore details from galaxies and related events.
- Streamline Workflows: Enhance investigative workflows by integrating MISP data for better situational awareness and time savings. For example, categorize related information within the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
- Foster Collaborative Threat Analysis: Collect, manage, and disseminate intelligence across organizations and with cybersecurity professionals based on the results. This facilitates a streamlined process and collaborative approach that spans the entire threat intelligence lifecycle—from collection and processing to analysis.
Maltego Graph also enables the visualization of the full MITRE ATT&CK framework, MISP Galaxies, and more. These capabilities not only reduce efforts but also ensure a more structured and efficient intelligence collection and analysis process, leading to quicker and more accurate threat detection and response.
Introducing Workflows 🔗︎
- Identify Suspicious Information: During your investigations, you may come across suspicious data such as domains, DNS names, email addresses, or IP addresses.
- Use MISP Transforms: Utilize MISP Transforms in Maltego Graph to analyze the above information.
- Look Up in MISP Community: From any type of Entity, query the MISP community.
- Check for Existing Records: Determine if the information has already been recorded in the MISP database to have additional context and insights into the data.
Demonstration 🔗︎
Below, you will find a simple investigation to learn how to leverage Maltego integration with MISP.
-
Step 1 – Starting with suspicious data
-
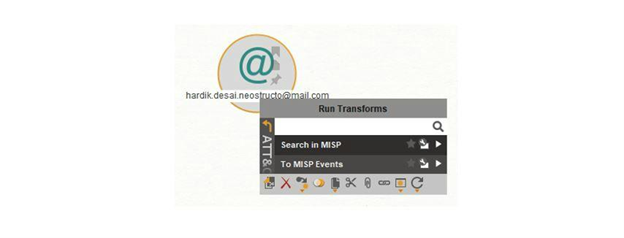
Overview: Let us start with an email address that a spam trap has detected. The given email source is hardik.desai.neostructo@mail[.]com. We will continue our investigation of this email address by adding it to a new graph. In the Transform menu, under the ATT&CK and MISP Transform group, use the To MISP Events Transform to find any related events.
-
Maltego task: Select the Phrase Entity containing the email address and run the following Transform:
-
-
Step 2 – Checking details for insights
-
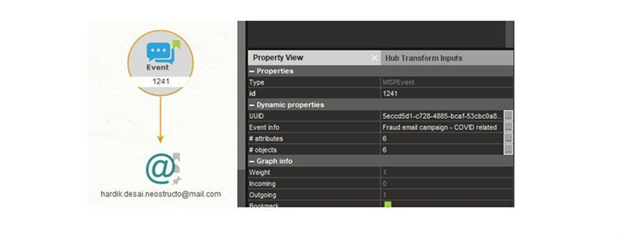
Overview: Sure enough, the email has already been recorded as an attribute of event ID 1241. The event info detailed in the Property View also indicates that it is associated with a COVID-related fraud email campaign. Additionally, there are six other attributes and objects linked to this event.
-
Maltego task: Check event details in Property View.
-
-
Step 3 – Checking other attributes of the event
-
Step 4 – Analyzing and classifying phishing threats
-
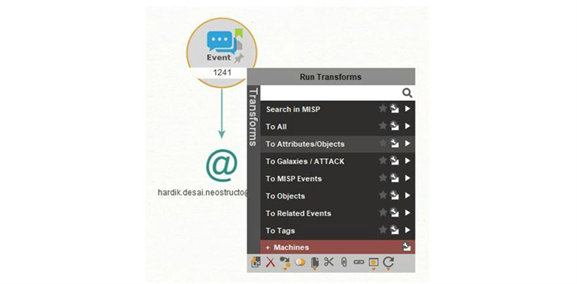
Overview: The previous step brought back the list of attributes and objects, including IP addresses, URLs, and domains, and a link to a VirusTotal report. From the Event Entity, there are various steps you could take to get more insights, such as finding related events or pulling a list of the tags.
-
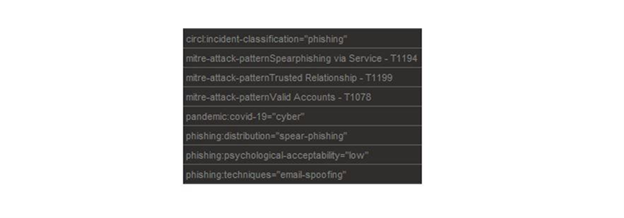
Maltego task: Run the Transform and switch it to List View to check phishing classification.
-
-
Step 5 – Mapping the patterns with MITRE ATT&CK
-
Overview: From the list, we can see that this event is classified as a cyber threat, specifically part of a spear-phishing campaign. It utilizes email spoofing, as shown in the List View image. The event is associated with some ATT&CK patterns. In this case, let’s explore the patterns using the MITRE ATT&CK framework data. By identifying these patterns, we can better protect ourselves against such attacks and test our incident readiness. First, check the details about the malware, software, and tools used in the attack technique. This information will help us understand the threat and improve our defensive strategies.
-
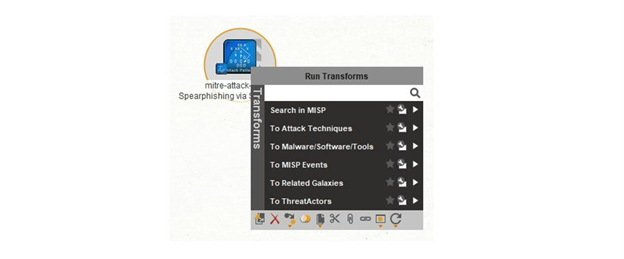
Malteg task: Select “mitre-attack-pattern Spearphishing via Service – T1194” Entity and run the following Transforms to look up the details
-
-
Step 6 – Exploring attack patterns
-
Overview: After checking the details, we can find other MISP events associated with this attack or search for specific threat actors known to use this attack pattern. This includes identifying which threat actors have utilized the pattern.
-
Maltego task: Run Transform:
-
-
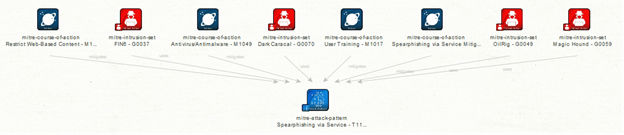
Step 7 – Exploring mitigation techniques
-
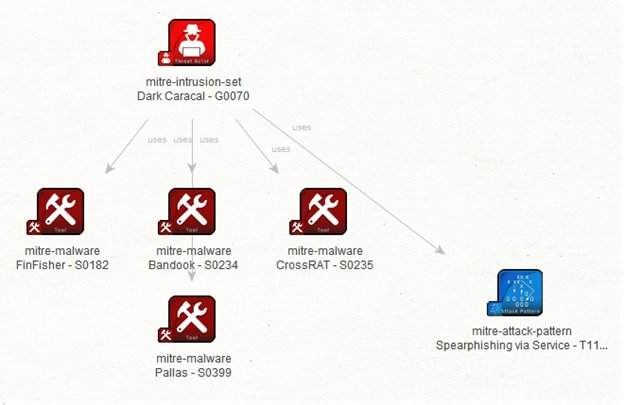
Overview: Now, we can discover suggested mitigation techniques to protect against this type of attack, such as using antivirus or antimalware software, performing user training, and restricting web-based content. For brevity, let’s look at one more example. Using the “To Malware/Software/Tools” Transform on the threat actor called Dark Caracal, we can identify the malware, software, and tools that this threat actor commonly uses.
-
Maltego task: Select threat actor and run the following Transform:
-
Voilà! The result reveals that Dark Caracal prefers to use FinFisher, Bandook, CrossRAT, and Pallas malware for their attacks. This demonstrates the extensive insights provided by integrating MITRE ATT&CK and MISP data using Maltego. The biggest advantage is the ability to extend and enrich investigations or uncover new IoCs through various data integrations without switching tools. To learn more about Maltego’s CTI-specific data integration, check our blog about Maltego Handbook for Cyber Threat Intelligence or simply download the handbook now.
Conclusion 🔗︎
The integration of Maltego with MISP supercharges analysts with unprecedented situational awareness for complex OSINT investigations. By leveraging Maltego’s visualization and data capabilities along with MISP’s extensive threat intelligence data, investigators can uncover hidden connections, enrich their findings, and streamline their workflows—all within the familiar Maltego interface. This powerful combination enhances the depth and efficiency of threat intelligence operations, providing a comprehensive toolset for effective data collection and threat analysis.
Download the resource
Stay connected with us on X and LinkedIn, and subscribe to our email newsletter to get updated with the latest news and developments.
Happy investigating!